A Molecular Portrait of ALS and FTD
Drug Target Review
AUGUST 9, 2023
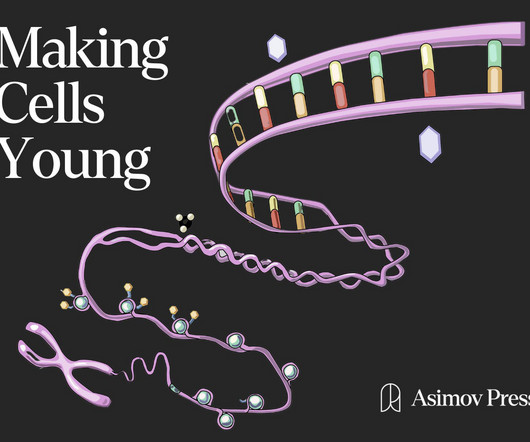
The specific proteins found in these aggregates can vary, but approximately 95 percent of ALS patients and 50 percent of FTD patients develop aggregates containing the TDP-43 protein (short for tar DNA binding protein 43). 14 TDP-43 is a DNA and RNA binding protein that regulates the expression and splicing of several target transcripts.





















Let's personalize your content