Reaching cruising altitude: New discovery tools to target RNA
Dark Matter Blog
AUGUST 31, 2020
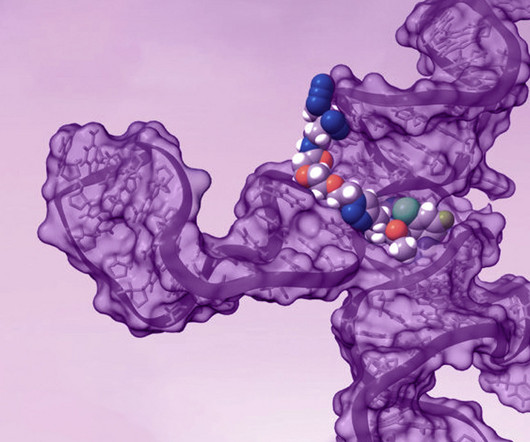
The majority of small molecule drugs induce their therapeutic effects by seeking out and binding to their intended target while avoiding most other molecules in the dense milieu of the cell interior. Our overall mission at Arrakis is to expand the set of “druggable” targets for small-molecule medicines to include RNA.











Let's personalize your content