Herpes virus might drive Alzheimer's pathology
Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JANUARY 2, 2025
Viral infections may play a role in Alzheimer's disease.
This site uses cookies to improve your experience. To help us insure we adhere to various privacy regulations, please select your country/region of residence. If you do not select a country, we will assume you are from the United States. Select your Cookie Settings or view our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use.
Cookies and similar technologies are used on this website for proper function of the website, for tracking performance analytics and for marketing purposes. We and some of our third-party providers may use cookie data for various purposes. Please review the cookie settings below and choose your preference.
Used for the proper function of the website
Used for monitoring website traffic and interactions
Cookies and similar technologies are used on this website for proper function of the website, for tracking performance analytics and for marketing purposes. We and some of our third-party providers may use cookie data for various purposes. Please review the cookie settings below and choose your preference.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JANUARY 2, 2025
Viral infections may play a role in Alzheimer's disease.

Drugs.com
JULY 10, 2024
TUESDAY, July 10, 2024 -- An experimental “air mask” could help ward off infectious diseases while people are on the job, researchers report.The mask uses an air curtain blowing down from the brim of a hard hat to prevent airborne viruses from rea.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Drugs.com
AUGUST 14, 2024
14, 2024 -- Parvovirus B19, a seasonal respiratory virus that subsided during the pandemic, is making a comeback, U.S. Centers for Disease Control and. WEDNESDAY, Aug. health officials warned Tuesday.In a health alert issued by the U.S.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JANUARY 1, 2025
Researchers have come up with a new way to identify more infectious variants of viruses or bacteria that start spreading in humans -- including those causing flu, COVID, whooping cough and tuberculosis.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JANUARY 30, 2025
Zika virus hijacks the skin of its human host to send out chemical signals that lure more mosquitoes to infect and spread the disease further, new research shows.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
DECEMBER 4, 2023
While we often think of diseases as caused by foreign bodies -- bacteria or viruses -- there are hundreds of diseases affecting humans that result from errors in cellular production of its proteins.
Drugs.com
MAY 8, 2024
WEDNESDAY, May 8, 2024 -- The virus behind COVID has mutated again, this time producing variants nicknamed FLiRT, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has reported.The variants are appearing in wastewater sampling, the CDC.
BioPharma Drive: Drug Pricing
JUNE 6, 2023
The biotech has raised about $65 million to test two ways to deliver larger genes into the body, each of which could help gene therapy treat more diseases.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
SEPTEMBER 19, 2024
A new study provides a list of the wildlife species present at the market from which SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, most likely arose in late 2019. The study is based on a new analysis of metatranscriptomic data released by the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).

Drugs.com
DECEMBER 1, 2023
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said that a surge in respiratory illnesses in China is not being fueled by a new. FRIDAY, Dec. 1, 2023 (Healthday News) -- In testimony provided Thursday to members of Congress, the head of the U.S.
Drugs.com
JUNE 29, 2023
THURSDAY, June 29, 2023 -- Americans ages 60 and up can get their vaccine for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) this fall, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention announced Thursday. On Thursday, Dr. Rochelle Walensky, the outgoing CDC.
Drugs.com
OCTOBER 2, 2023
2, 2023 -- New research shows the COVID-19 virus can directly infect coronary arteries, inflaming fatty plaque inside them, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. MONDAY, Oct. This may explain why some people who get COVID-19 have.
Drugs.com
NOVEMBER 12, 2024
12, 2024 -- A cutting-edge genetic test can rapidly detect and identify almost any kind of disease-causing microorganism in the human body, whether it’s a virus, bacteria, fungus or parasite, researchers say.Doctors have been using t. TUESDAY, Nov.
Drugs.com
APRIL 17, 2024
WEDNESDAY, April 17, 2024 -- In a new study, people living with HIV who got standard meds to keep the virus at bay also had much lower rates of Alzheimer's disease -- suggesting the drugs might also lower risks for the brain illness.It's.

Drugs.com
AUGUST 15, 2023
15, 2023 -- Mosquitoes can be a big pest, leaving behind itchy bumps on skin and potentially spreading serious diseases, such as West Nile virus. Sam Telford III is a professor of infectious disease and global health at Cummings School. TUESDAY, Aug.

BioPharma Drive: Drug Pricing
MAY 7, 2024
The company is using what it claims is the largest database of viral protein structures to unearth medicines for a range of diseases, said CEO and Flagship origination partner Lovisa Afzelius.
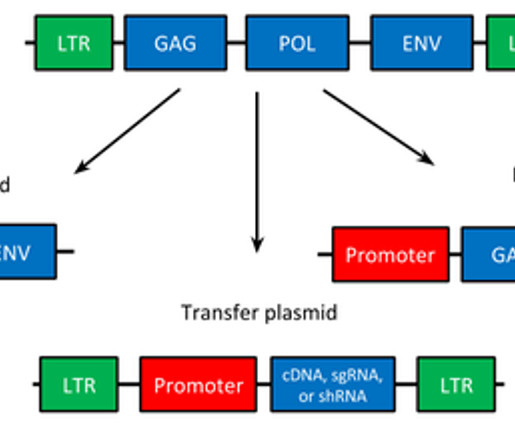
addgene Blog
JUNE 22, 2023
Some of these viruses are completely inert, but others can cause diseases. Viruses have become a regular part of basic biological research as well as clinical therapy. These biological tools are useful because they ’ re derived from viruses that can infect people, cells, and animals. Nervous about handling viruses? That ’ s okay!

Drugs.com
SEPTEMBER 7, 2023
7, 2023 -- While it doesn't prevent infection altogether, new research shows the mpox vaccine does reduces the severity of disease in those who fall ill from the virus. THURSDAY, Sept. An international team of scientists found that those people who.

Covalent Modifiers
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
4c15843 Peptide macrocycles are promising therapeutics for a variety of disease indications due to their overall metabolic stability and potential to make highly selective binding interactions with targets. Boyd, Lei Wang, Ralf Bartenschlager, and Matthew Bogyo Journal of the American Chemical Society 2025 DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c15843
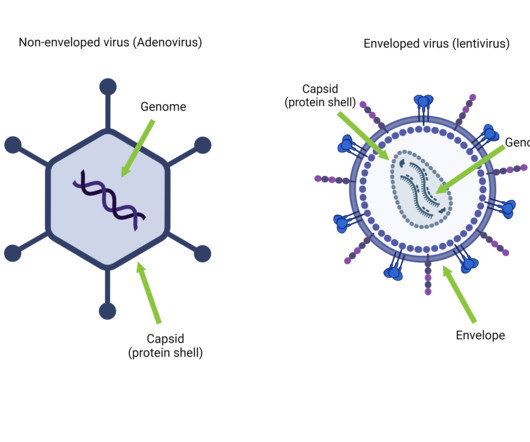
addgene Blog
AUGUST 18, 2023
Yet these simple, small particles have quite the outsized impact – and not just on the disease front. Viruses are simple – a genome packaged in a protein shell (Taylor, 2014). They’re so simple that we can’t even decide if they’re alive or not.

Drugs.com
AUGUST 4, 2023
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on Thursday recommended that all infants under the age of 8 months be given a new antibody shot to help guard against severe respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). FRIDAY, Aug. 4, 2023 – The U.S. The antibody.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
AUGUST 9, 2023
The drug tecovirimat is currently in use for the treatment of mpox -- the disease caused by monkeypox virus -- that spread worldwide in 2022. Tecovirimat is an anti-poxviral drug, and its use is driving the emergence of drug-resistant variants of the monkeypox virus.
Drugs.com
JANUARY 7, 2025
7, 2025 -- That cold sore on your lip might be painful and unsightly, but it could also be a harbinger of debilitating brain aging.The oral herpes virus appears to be linked with Alzheimers disease, suggesting that the common i. TUESDAY, Jan.

Chemical Biology and Drug Design
DECEMBER 13, 2023
These strategies act by taking advantage of the weakness points of this attractive bioweapon to disable or attack it (itself), accordingly stop the entire viral reproduction, and effectively end the severe microbial infections such as the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). SARS-CoV-2) to infect humans and spread infections.

ASPET
APRIL 2, 2024
Bromine domain protein 2 (BRD2), a member of the Bromodomain and extraterminal domain (BET) protein family, is a crucial epigenetic regulator with significant function in various diseases and cellular processes. Notably, the potential role of BRD2 as a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target is discussed in the context of various diseases.

Chemical Biology and Drug Design
APRIL 18, 2023
The severity of chagas disease remains a major concern in endemic areas and an emerging public health hazard in nonendemic countries. Abstract Twenty different infectious disorders induced by bacteria, viruses, and parasites are categorized as neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) by WHO.
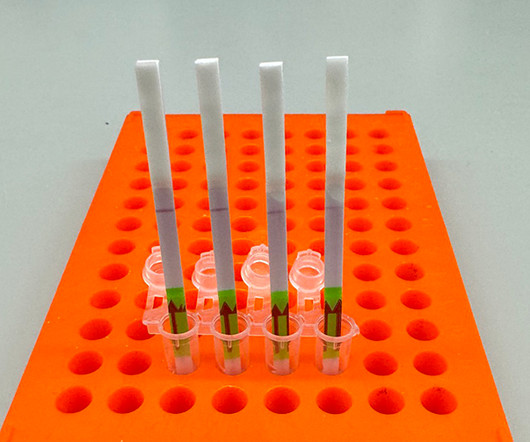

Broad Institute
JUNE 18, 2024
Simple test for flu could improve diagnosis and surveillance By Allessandra DiCorato June 18, 2024 Breadcrumb Home Simple test for flu could improve diagnosis and surveillance A low-cost CRISPR-based paper strip test distinguishes between influenza types and can be reprogrammed to recognize different viruses including the H5N1 bird flu virus.

Broad Institute
JANUARY 8, 2024
Williams January 8, 2024 Credit: Susanna Hamilton, Broad Communications Researchers have developed virus-like particles that can deliver gene-editing cargo to cells, including those in the mouse brain. Delivery dilemma Gene editing approaches promise to treat a range of diseases by precisely correcting genetic mutations that cause disease.

PLOS: DNA Science
JANUARY 25, 2024
A recent report in PLOS ONE analyzes DNA from an adenovirus and a herpes virus discovered in preserved feces – coprolites – from 5,500 to 7,000 years ago at an archaeological site in Japan. The post Chewing Gum Reveals Stone Age Diet and Disease appeared first on DNA Science.

Broad Institute
JUNE 25, 2024
If you only study a small, homogeneous population, you will probably miss something," said co-corresponding author Daniel (Dong) Wang, an assistant professor of medicine at Brigham and Women's Hospital and of nutrition at Harvard Chan School, and an associate member of Broad's Infectious Disease and Microbiome Program (IDMP).
Drugs.com
JUNE 29, 2023
THURSDAY, June 29, 2023 -- Americans ages 60 and up can get their vaccine for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) this fall, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention announced Thursday. On Thursday, Dr. Rochelle Walensky, the outgoing CDC.

SCIENMAG: Medicine & Health
JANUARY 5, 2024
When the body encounters bacteria, viruses or harmful substances, its innate immune cells, neutrophils, assemble at the site to combat the invader. Credit: UofL photo. When the body encounters bacteria, viruses or harmful substances, its innate immune cells, neutrophils, assemble at the site to combat the invader.
SCIENMAG: Medicine & Health
AUGUST 10, 2023
Viral infections, autoimmune disease, and other conditions can cause platelet levels to drop throughout the body, termed thrombocytopenia. CHAPEL HILL, N.C. Platelets, or thrombocytes, are specialized cellular fragments that form blood clots when we get scrapes and traumatic injuries. Platelets, or […]

Drugs.com
SEPTEMBER 6, 2023
6, 2023 -- Doctors are seeing a spike in severe cases of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) among young children in Florida and Georgia, U.S. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention sent an. WEDNESDAY, Sept. health officials warned Tuesday.
Broad Institute
MAY 16, 2024
The enormous challenge of getting therapies past this barrier — a highly selective membrane separating the blood from the brain — has stymied the development of safer and more effective gene therapies for brain diseases for decades.

The Pharma Data
MARCH 23, 2022
To treat Ebola virus infections, researchers are taking a close look at a key piece of the virus: polymerase. Polymerase is a viral protein that directs how Ebola virus replicates its genome as it infects new hosts. Drugs that target polymerase could potentially treat Ebola virus infections and save lives.

ProRelix Research
SEPTEMBER 7, 2023
Autoimmune disorders comprise several diseases in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the body’s own healthy cells instead of destroying bacteria and viruses to keep the body healthy. […] The post Autoimmune disorders and current developments of novel treatments under clinical trials appeared first on ProRelix Research.

SCIENMAG: Medicine & Health
JULY 27, 2023
OVX836 demonstrated positive safety and immunogenicity data across three dose levels A notable signal of protection of 84% was observed against symptomatic influenza infection Lyon, France – July 28, 2023 – Osivax, a biopharmaceutical company developing vaccines to provide broad-spectrum protection against highly mutating infectious viruses, today (..)

SCIENMAG: Medicine & Health
OCTOBER 24, 2023
Mosquitoes and other insects can carry human diseases such as dengue and Zika virus, but when those insects are infected with certain strains of the bacteria Wolbachia, this bacteria reduces levels of disease in their hosts. Humans currently take advantage of this to control harmful virus populations across the world.

Drug Target Review
AUGUST 11, 2023
In a new development, a recent paper published in Biology Methods & Protocols by Oxford University Press has highlighted a promising avenue for enhancing vaccine efficacy against infectious pathogens like the COVID-19 virus. Since December 2019, SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection has become a worldwide urgent public health concern.

ASPET
JULY 19, 2023
Several ongoing investigations have associated G3BPs with a number of disease states including cancer progression, invasion, metastasis, and viral infection and have highlighted its potential as a target for cancer therapeutic agents.

The Pharma Data
MAY 5, 2022
In animal studies that mimic human exposures, an investigational COVID vaccine designed to be taken orally not only protects the host, but also decreases the airborne spread of the virus to other close contacts. Because of this, they did not shed as much virus through normal airborne exposures. Langel, Ph.D., Source link: [link].

Broad Institute
JUNE 10, 2024
The advance, from the lab of Broad core institute member David Liu , could one day help researchers develop a single gene therapy for diseases such as cystic fibrosis that are caused by one of hundreds or thousands of different mutations in a gene.

SCIENMAG: Medicine & Health
AUGUST 7, 2023
Several diseases are caused by viruses, bacteria, or even parasites. Sometimes, these microorganisms cannot infect humans (or other animals) by themselves, so they rely on other organisms -called vectors- to carry them around and transmit the disease from one host to another. A well-known group of vectors is arthropods.
Expert insights. Personalized for you.
We have resent the email to
Are you sure you want to cancel your subscriptions?


Let's personalize your content