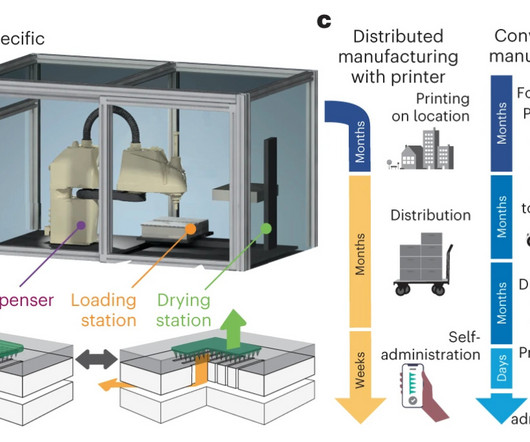
The role of CRISPR in microbiome engineering breakthroughs
Drug Target Review
JUNE 28, 2023
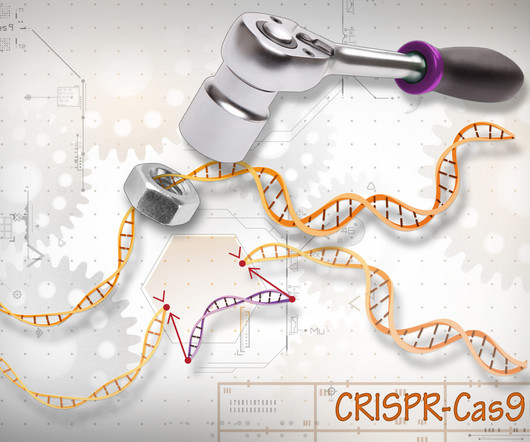
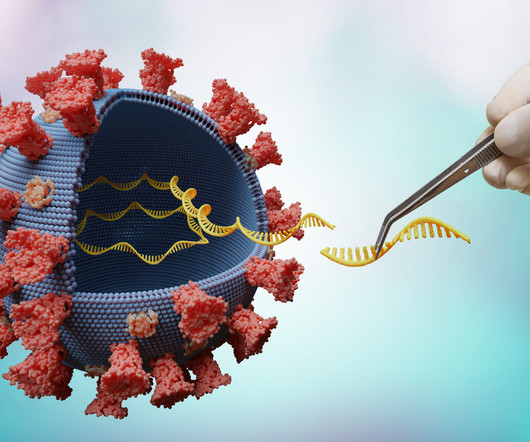
When faced with a viral threat, bacterial cells developed an immune response by capturing and copying DNA fragments of viruses. This allowed bacteria to recognise subsequent attacks and cleave the viral DNA to stop the viral infection. It was also discovered that the Cas enzyme was responsible for DNA cleavage.



























Let's personalize your content