U.S. Postpartum Depression Diagnoses Doubled in a Decade
Drugs.com
NOVEMBER 20, 2024
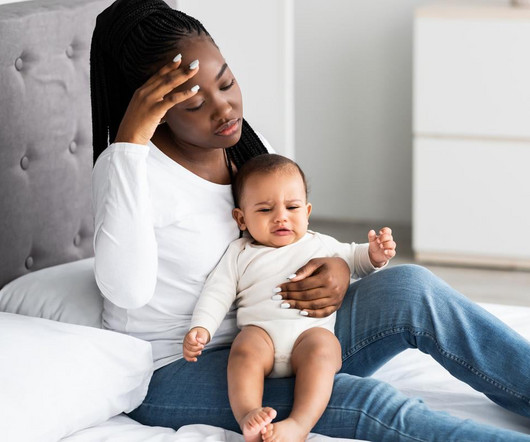
WEDNESDAY, Nov. 20, 2024 -- Rates of postpartum depression have more than doubled in little over a decade among American women, a new analysis shows. While about 1 in every 10 new moms (9.4%) suffered postpartum depression in 2010, that number rose.










































Let's personalize your content