We date, marry people who are attractive as we are, new analysis finds
Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JUNE 27, 2024
Men and women were good at judging their own attractiveness, and tended to partner up with people who were similarly attractive.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JUNE 27, 2024
Men and women were good at judging their own attractiveness, and tended to partner up with people who were similarly attractive.

BioPharma Drive: Drug Pricing
JUNE 27, 2024
A growing cohort of biotechs, from Biohaven to Neurocrine to Jazz, hope research on ion channels will bring them new drugs and big business — much like it has done for Vertex.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JUNE 27, 2024
Researchers have developed a tiny robot replicating the aerial dance of falling maple seeds. In the future, this robot could be used for real-time environmental monitoring or delivery of small samples even in inaccessible terrain such as deserts, mountains or cliffs, or the open sea. This technology could be a game changer for fields such as search-and-rescue, endangered species studies, or infrastructure monitoring.
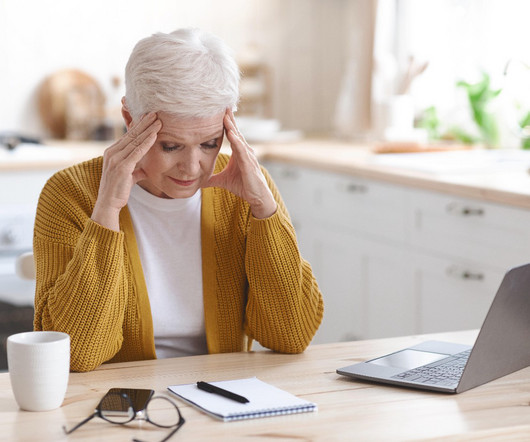

Drugs.com
JUNE 27, 2024
THURSDAY, June 27, 2024 -- It's a nasty cycle: Chronic migraine sufferers who use too much pain medication sometimes get smacked with rebound headaches. But new research suggests that a medication commonly used to prevent migraines may also help.

Speaker: Simran Kaur, Co-founder & CEO at Tattva.Health
AI is transforming clinical trials—accelerating drug discovery, optimizing patient recruitment, and improving data analysis. But its impact goes far beyond research. As AI-driven innovation reshapes the clinical trial process, it’s also influencing broader healthcare trends, from personalized medicine to patient outcomes. Join this new webinar featuring Simran Kaur for an insightful discussion on what all of this means for the future of healthcare!

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JUNE 27, 2024
H5N1 virus in unpasteurized milk is stable on metal and rubber components of commercial milking equipment for at least one hour, increasing its potential to infect people and other animals.
Drug Discovery Digest brings together the best content for drug research and development professionals from the widest variety of industry thought leaders.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JUNE 27, 2024
Older coastal cities, like Philadelphia, New York and Boston are at risk of being inundated by untreated sewage during floods. Due in part to the design of their combined sewer systems and in part due to sea level rise, these cities could be facing a growing public health crisis as climate change also drives more extreme precipitation. The group recently published research that modeled the potential extent of the problem in a section of the coastal city of Camden, New Jersey, and the effectivene

Drugs.com
JUNE 27, 2024
THURSDAY, June 27, 2024 -- Acupuncture can help breast cancer patients deal with the hot flashes that often accompany hormone therapy, a new clinical trial says.Nearly 2 in 3 women who got acupuncture during hormone therapy reported fewer and less.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JUNE 27, 2024
Why did multicellularity arise? Solving that mystery may help pinpoint life on other planets and explain the vast diversity and complexity seen on Earth today, from sea sponges to redwoods to human society. A new article shows how specific physical conditions -- especially ocean viscosity and resource deprivation -- during the global glaciation period known as Snowball Earth could have driven eukaryotes to turn multicellular.

Drugs.com
JUNE 27, 2024
THURSDAY, June 27, 2024 -- Many sexually transmitted diseases are on the rise in the United States, and a nationwide poll indicates that ignorance about how they're transmitted could be fueling their spread.About a third of Americans (34%) falsely.

Speaker: Simran Kaur, Founder & CEO at Tattva Health Inc.
The healthcare landscape is being revolutionized by AI and cutting-edge digital technologies, reshaping how patients receive care and interact with providers. In this webinar led by Simran Kaur, we will explore how AI-driven solutions are enhancing patient communication, improving care quality, and empowering preventive and predictive medicine. You'll also learn how AI is streamlining healthcare processes, helping providers offer more efficient, personalized care and enabling faster, data-driven

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JUNE 27, 2024
Mathematicians ave put forward a hypothesis which suggests that the reason male mammals don't breastfeed might be driven by the rich community of microbes that lives in breast milk and which plays an important part in establishing the gut microbiome of the infant.

Collaborative Drug
JUNE 27, 2024
Vault Snack #24 - New Interface, Features & Infrastructure for the CDD Vault ELN

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JUNE 27, 2024
Scientists shed light on an unexpected partnership: A marine diatom and a bacterium that can account for a large share of nitrogen fixation in vast regions of the ocean. This symbiosis likely plays a key role for global marine nitrogen fixation and productivity, and thus uptake of carbon dioxide. The newly-discovered bacterial symbiont is closely related to the nitrogen-fixing Rhizobia which live in partnership with many crop plants and may also open up new avenues for engineering nitrogen-fixin

Drugs.com
JUNE 27, 2024
THURSDAY, June 27, 2024 -- Just 25% of people battling opioid use disorder are getting medications aimed at helping them quit and potentially avoid an overdose, new data shows. Boosting access to proper treatment might save countless lives. "In.

Advertisement
Clinical trial data management is increasingly challenging as studies grow in complexity. Quickly accessing and analyzing study data is vital for assessing trial progress and patient safety. In this paper, we explore real-time data access and analysis for proactive study management. We investigate using adverse event (AE) data to monitor safety and discuss a clinical analytics platform that supports collaboration and data review workflows.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JUNE 27, 2024
The last population of woolly mammoths was isolated on Wrangel Island off the coast of Siberia 10,000 years ago, when sea levels rose and cut the mountainous island off from the mainland. A new genomic analysis reveals that the isolated mammoths, who lived on the island for the subsequent 6,000 years, originated from at most 8 individuals but grew to 200--300 individuals within 20 generations.
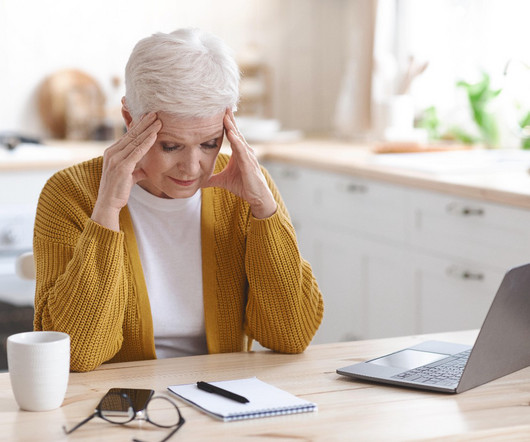

Drugs.com
JUNE 27, 2024
THURSDAY, June 27, 2024 -- It's a nasty cycle: Chronic migraine sufferers who use too much pain medication sometimes get smacked with rebound headaches.But new research suggests that a medication commonly used to prevent migraines may also help.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JUNE 27, 2024
Researchers have described some of the best-preserved three-dimensional trilobite fossils ever discovered. The fossils, which are more than 500 million years old, were collected in the High Atlas of Morocco and are being referred to by scientists as 'Pompeii' trilobites due to their remarkable preservation in ash.

BioPharma Drive: Drug Pricing
JUNE 27, 2024
The pharma’s acquisition of Celsius is the latest in a string of deals by major drugmakers hunting anti-inflammatory medicines.

Advertisement
Clinical research has entered a new era, one that requires real-time analytics and visualization to allow trial leaders to work collaboratively and to develop, at the click of a mouse, deep insights that enable proactive study management. Learn how Revvity Signals helps drug developers deliver clinical trial data insights in real-time using a fast and flexible data and analytics platform to empower data-driven decision-making.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JUNE 27, 2024
By restricting radiant heat flows between buildings and their environment to specific wavelengths, coatings engineered from common materials can achieve energy savings and thermal comfort that goes beyond what traditional building envelopes can achieve.
Drugs.com
JUNE 27, 2024
THURSDAY, June 27, 2024 -- In new vaccination guidance issued Wednesday, U.S. health officials now recommend that all Americans aged 75 and older get an RSV vaccine before fall arrives.However, those a bit younger -- ages 60 to 74 -- should only.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JUNE 27, 2024
Across the Midwest during the warmer months, studying the sky for signs of storms and tornadoes becomes one of the most popular pastimes. Working at the intersection of climate science and meteorology and using modeling, scientists are looking at the big picture of what causes severe storms and tornadoes -- and what dictates where they occur.

Drugs.com
JUNE 27, 2024
THURSDAY, June 27, 2024 -- As psilocybin mushrooms become the most popular psychedelic in the United States, some states have started to ease regulations on its recreational use. Now, a new report warns that the federal government will have to.

Advertisement
Clinical development organizations face a wide array of challenges when it comes to data, many of which can impact the operational effectiveness of their clinical trials. In this whitepaper, experts from Revvity Signals explore how solutions like TIBCO® Spotfire® enable better, more streamlined studies. The whitepaper also features a success story from Ambrx, a leading biopharmaceutical company, detailing how it has leveraged Spotfire to tackle data quality and collaboration challenges in clinic

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JUNE 27, 2024
In a rare opportunity to study carnivores before and after wolves were reintroduced to their ranges, researchers found that the effects of wolves on Isle Royale have been only temporary. And even in the least-visited national park, humans had a more significant impact on carnivores' lives.

BioPharma Drive: Drug Pricing
JUNE 27, 2024
The new guidance more strongly urges vaccination in adults who are older or at higher risk, but removes a prior recommendation for adults aged 60 to 74 years without certain risk factors.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JUNE 27, 2024
Slush -- water-soaked snow -- makes up more than half of all meltwater on the Antarctic ice shelves during the height of summer, yet is poorly accounted for in regional climate models. The findings could have profound implications for ice shelf stability and sea level rise.
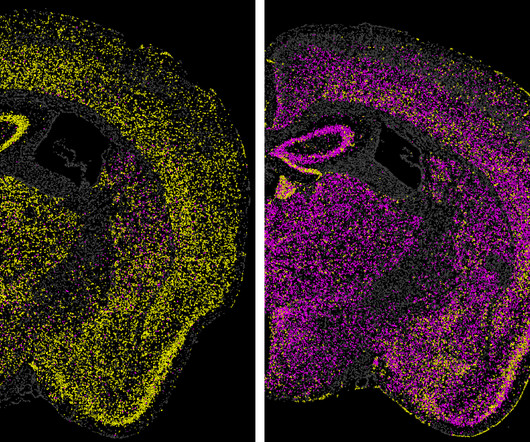
Broad Institute
JUNE 27, 2024
A therapy candidate for fatal prion diseases turns off disease-causing gene By Corie Lok June 27, 2024 Breadcrumb Home A therapy candidate for fatal prion diseases turns off disease-causing gene Whitehead and Broad scientists have developed a gene-silencing tool that could pave the way for a new class of genetic approaches to treat certain diseases.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
JUNE 27, 2024
The majority of stars in our galaxy are home to planets. The most abundant are the sub-Neptunes, planets between the size of Earth and Neptune. Calculating their density poses a problem for scientists: depending on the method used to measure their mass, two populations are highlighted, the dense and the less dense. Is this due to an observational bias or the physical existence of two distinct populations of sub-Neptunes?
Let's personalize your content